SBPMD Histology Laboratory Manual
Cervix Uteri
#67 Cervix, Human
Open with WebViewer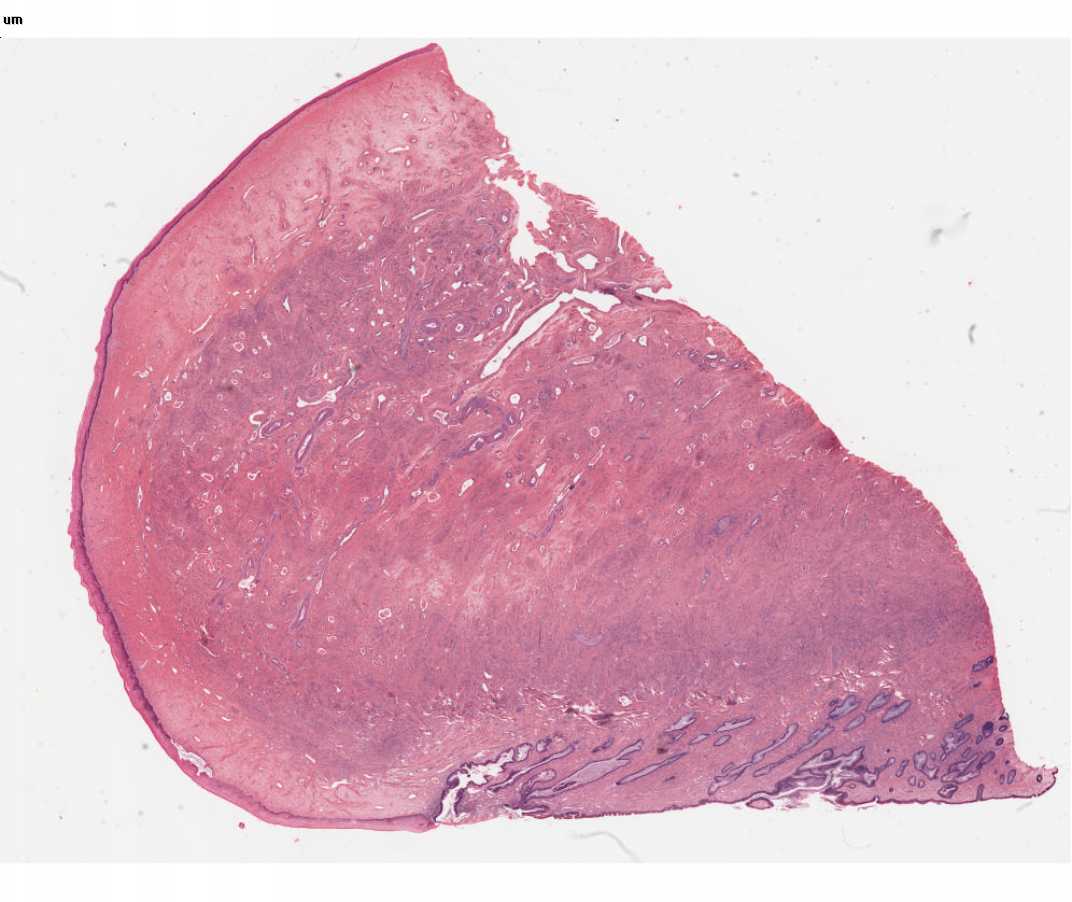
Distinguish (1) the endocervix, the region lined by typical cervical epithelium and containing glands, and (2) the ectocervix, that portion of the cervix projecting into the vaginal lumen which is lined by a thickened, basophilic, stratified squamous epithelium. Locate at higher magnification some of the mucus-secreting epithelial cells, which line the cervical mucosa. Note the pale-staining, supra-nuclear areas in these cells. These regions are occupied by abundant mucoprotein granules, which would be stained magenta if the periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) technique had been applied to the slides rather than H&E. Note also the abrupt transition between the simple columnar epithelium of the cervix and the stratified squamous epithelium of the portio vaginalis of the cervix (the transformation zone). The bulk of the wall of the cervix is made up of bundles of smooth muscle interlaced with connective tissue.
What are some of the possible functions of cervical mucus?
In what other regions of the body does one observe an abrupt junction between simple columnar and stratified epithelia?